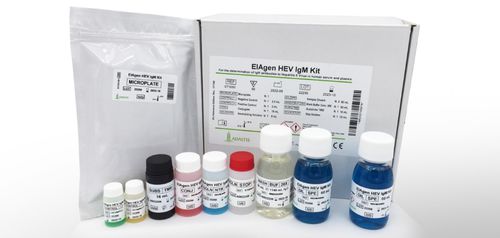
Hepatitis E test kit EIAgenIgMHCVHBV
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Applications
- hepatitis E
- Tested parameter
- IgM
- Micro-organism
- HCV, HBV, HEV
- Sample type
- plasma, stool
- Analysis mode
- ELISA
Description
Enzyme ImmunoAssay (ELISA) for the determination of IgM antibodies to Hepatitis E Virus in human plasma and sera. The kit may be used for the follow-up of HEV-infected patients. For “in vitro” diagnostic use only.
Introduction
Hepatitis E Virus or HEV is a recently discovered agent of enterically transmitted viral hepatitis. HEV is an unenveloped single-strand RNA virus structurally similar to Calicivirus and is found in the stool of infected patients.
HEV is a serious problem in many developing countries and its first outbreak was reported in 1955 in New Delhi, India.
Hepatitis E has never been associated with chronic infection; however a high case-fatality rate has been found among pregnant women.
The cloning and sequencing of HEV genome have lead to the development of serological tests for the detection of anti HEV antibodies.
These tests are based on synthetic immunodominant antigens derived from conservative regions of the virus.
Tests for IgM are used to determine the nature of the infective agent in patients showing symptoms of hepatitis, in order to rule out the possibility of other most severe viral infections (HBV, HDV, HCV).
Principle of the Method
Microplates are coated with HEV-specific synthetic antigens encoding for conservative and immunodominant determinants derived from ORF2 and ORF3 of all the 4 subtypes.
The solid phase is first treated with the diluted sample and anti HEV IgM are captured, if present, by the antigens adsorbed on wells.
After washing out all the other components of the sample, in the 2nd incubation bound anti HEV IgM antibodies are detected by the addition of polyclonal specific anti IgM antibodies,
Related Searches
- Assay kit
- Solution reagent kit
- Blood assay kit
- Molecular biology reagent kit
- Serum assay kit
- Immunoassay assay kit
- Plasma assay kit
- Infectious disease detection kit
- Diagnostic reagent kit
- Molecular test kit
- Respiratory infection test kit
- Whole blood detection kit
- Optical assay kit
- Clinical assay kit
- Dye reagent
- Buffer solution reagent kit
- Fluorescence assay kit
- COVID-19 detection kit
- ELISA assay kit
- Real-time PCR test kit
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.