- Laboratory
- Laboratory medicine
- Staining solution reagent
- BIO-OPTICA Milano
- Company
- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
Staining solution reagent Brown-Brenn for histologyfor cytology
Add to favorites
Compare this product
fo_shop_gate_exact_title
Characteristics
- Type
- staining solution
- Applications
- for histology, for cytology
Description
Minimum number of tests that can be performed 100
Completion time 8 minutes
Shelf life 2 years
Storage conditions 15-25°C
Additional equipment Not required
Application
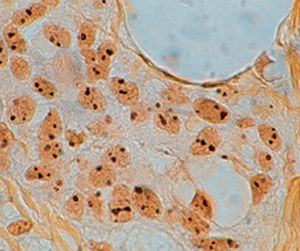
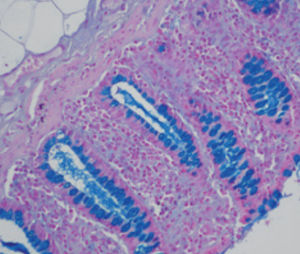
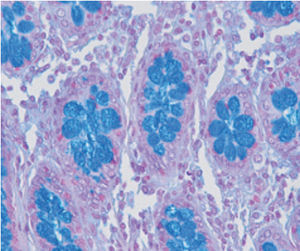
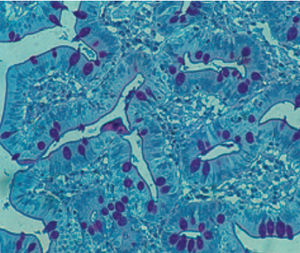
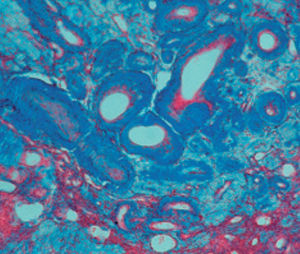
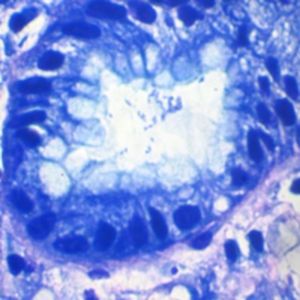
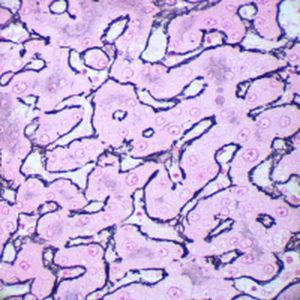
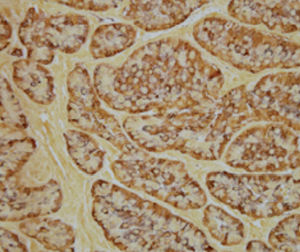
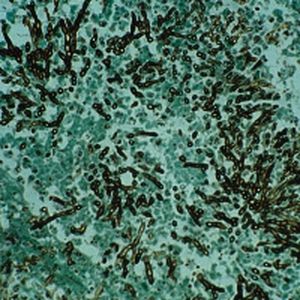
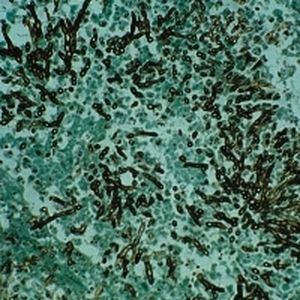
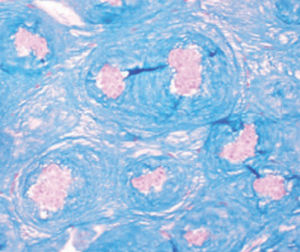
Method for differentiating Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria on histological
sections and smears.
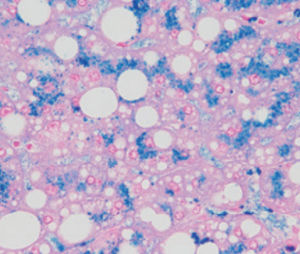
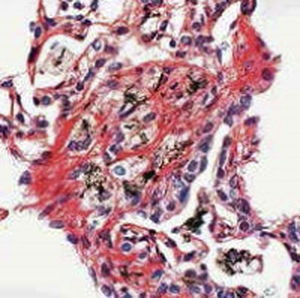
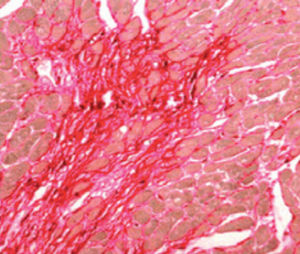
Result
Gram-positive bacteria blue
Gram-negative bacteria red
Actinomycetes (Nocardia) blue
Nuclei red
Other tissue elements yellow
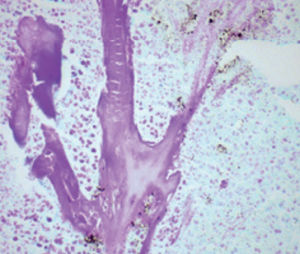
Product for the preparation of cyto-histological samples for optical microscopy.
For demonstration Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in tissue sections and smears.
PRINCIPLE
Gram staining is the most important method to differentiate bacteria species. Two dyes are used one after the other: crystal violet and fuchsine. Crystal violet solution precipitates through oxidation with a iodine solution. The deriving complex attaches
to bacteria cell walls with bonds of varying nature and intensity. The differentiating solution removes the crystal violet-iodine complex from the walls of some bacteria, but it does not act on others. These retain the primary dye and are called Gram- positive. Decolorized bacteria are then counterstained with a red dye; they are called Gram negative. Gram-positive bacteria’s capacity to retain the dye-iodine complex is usually ascribed to the bond which develops between the complex and a molecule only Gram-positive possess, namely magnesium ribonucleate.
The product is intended for professional laboratory use for healthcare professionals.
Carefully read the information on the label (danger symbols, Nrisk and safety phrases) and always consult the safety data sheet. Do not use if the primary container is damaged.
Catalogs
General Catalogue
164 Pages
Related Searches
- Bio-Optica solution reagent
- Laboratory reagent kit
- Bio-Optica histology reagent
- Reagent medium reagent kit
- Bio-Optica stain reagent
- Bio-Optica cytology reagent
- Buffer solution reagent kit
- Bacteria reagent kit
- Bio-Optica staining solution reagent
- Microscope slide
- Sample preparation reagent kit
- Pathology reagent
- Bilirubin reagent kit
- Bio-Optica fixative solution reagent
- Paraffin wax reagent
- Phosphate buffer reagent kit
- Collagen reagent kit
- Helicobacter pylori reagent kit
- Microscopy reagent
- Decalcifying solution reagent
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.