Website:
Bioquochem
Website:
Bioquochem
All Bioquochem products
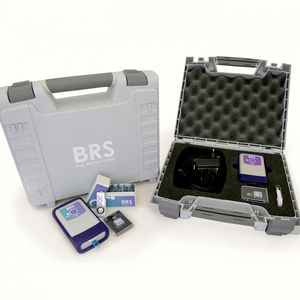
BRS (BQC Redox System)
BRS Accessories
Antioxidant Capacity
ABTS assay kit KF01002
for oxidative stress
for research
total antioxidant status
€200
-
€500
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
FRAP assay kit KF01003
for clinical chemistry
total antioxidant status
plasma
€220
-
€500
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
ORAC assay kit KF1004
for clinical chemistry
total antioxidant status
vitamin
€250
-
€600
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *

CUPRAC assay kit KF01005
for clinical chemistry
total antioxidant status
€200
-
€520
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
FRAP assay kit KF01006
for clinical chemistry
total antioxidant status
plasma
€190
-
€350
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
DPPH assay kit KF01007
for clinical chemistry
total antioxidant status
€170
-
€410
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
Biomolecule damage assays

TBARS-MDA assay kit KB03016
for oxidative stress
for lipid peroxidation
malondialdehyde
€220
-
€520
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *

oxidative stress assay kit KB03038
hydrogen peroxide
biological
enzymatic
€300
-
€830
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *

oxidative stress assay kit KB03010
nitrite
nitrate
for molecular biology
€350
-
€830
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
Enzymatic Assays

superoxide dismutase assay kit KB03011
for oxidative stress
hydrogen peroxide
uric acid
€280
-
€470
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *

catalase activity assay kit KB03012
for oxidative stress
hydrogen peroxide
biological
€300
-
€670
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *

xanthine oxidase activity assay kit KB03032
for oxidative stress
hydrogen peroxide
uric acid
€300
-
€750
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
Phenolic Compounds
anthocyanin assay kit KB03015
for oxidative stress
food intolerance
cell
€120
-
€290
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *

proanthocyanidins assay kit KB03017
for identification analysis
for food
colorimetric
€150
-
€360
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
oxidative stress assay kit KB03006
total antioxidant status
polyphenol
€210
-
€390
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
ROS Detection
Sample pretreatment

ponceau S stain reagent SP04001
staining solution
for Western blot
protein
€73
Indicative price excl. tax *
Indicative price excl. tax *

solution reagent kit KB03005
for protein analysis
for protein concentration
total proteins
€170
-
€270
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *

cellular biology assay kit KB03029
total antioxidant status
for biological samples
€190
-
€410
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *

cellular biology assay kit KB03027
total antioxidant status
for biological samples
€190
-
€400
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *

clinical chemistry assay kit KB03031
total antioxidant status
laboratory
biochemical
€290
-
€730
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
Stain line
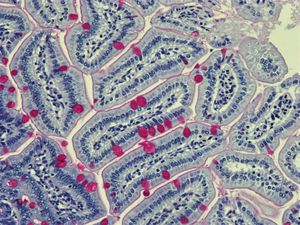
Harris hematoxylin reagent kit KH07012
for research
clinical
colorimetric
€130
-
€290
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
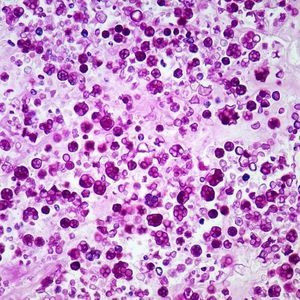
Mayer’s hematoxylin-Eosin reagent kit KH07011
for histology
for research
clinical
€130
-
€290
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
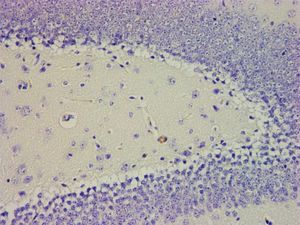
hématoxyline de Mayer reagent kit KH07008
immunohistochemistry
acetic acid
€49
-
€110
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
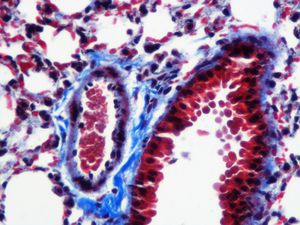
Masson’s trichrome reagent kit KH07007
for research
for histology
acetic acid
€180
-
€390
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
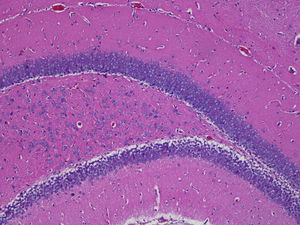
Harris hematoxylin reagent kit KH07005
for research
for histology
acetic acid
€120
-
€270
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
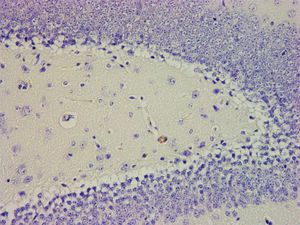
hématoxyline de Mayer reagent kit KH07004
for research
for histology
acetic acid
€120
-
€270
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
Harris hematoxylin reagent kit KH07003
staining solution
for research
for histology
€49
-
€110
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
Gomori trichrome reagent kit KH07002
for research
for histology
acetic acid
€180
-
€400
Price excl. tax *
Price excl. tax *
Remove all
Compare up to 10 products