- Laboratory
- Laboratory medicine
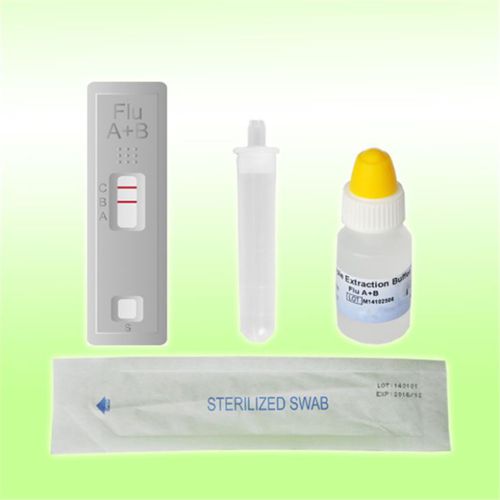
- Rapid flu test
- Boson Biotech Co., Ltd.
Rapid flu test 1N18C5for antigensinfluenza Ainfluenza B
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Applications
- flu
- Tested parameter
- for antigens
- Micro-organism
- influenza A, influenza B
- Sample type
- nasal, nasopharyngeal, cell
- Analysis mode
- immunochromatographic
- Format
- cassette
- Result display time
15 min
Description
Rapid Influenza A+B Test is an in vitro immunochromatographic assay for the qualitative detection of influenza type A and type B nucleoprotein antigens in nasopharyngeal swab, nasal swab and nasal aspirate samples. The identification is based on the monoclonal antibodies specific for the nucleoprotein of Influenza virus A. It is intended to aid in the rapid diagnosis of influenza infection. Negative results should be confirmed by other methods, such as cell culture.
Flu, or influenza, is a contagious respiratory infection caused by a variety of flus viruses. Symptoms of flu involve muscle aches and soreness, headache, and fever. Types A and B influenza are the more common forms of this infection, routinely causing seasonal outbreaks. Type B influenza can be just as severe as type A influenza but is less common throughout the flu season compared to type A. Unlike a type B infection, type A viruses are categorized by subtypes and strains. Influenza A mutates faster than influenza B, but both viruses are always changing, creating new strains form one flu season to the next.
Catalogs
Influenza
2 Pages
Other Boson Biotech Co., Ltd. products
Infectious Diseases Test Kits
Related Searches
- Blood rapid diagnostic test
- Rapid lateral flow test
- Immunoassay rapid diagnostic test
- Cassette rapid diagnostic test
- Rapid virus test
- Serum rapid diagnostic test
- Plasma rapid diagnostic test
- Infectious disease rapid diagnostic test
- Whole blood rapid diagnostic test
- Rapid respiratory infection test
- Urine rapid diagnostic test
- Virus reagent kit
- COVID-19 rapid diagnostic test
- Test strip
- Bacteria rapid diagnostic test
- Strip rapid diagnostic test
- Microbiology reagent kit
- Rapid feces test
- Rapid drug abuse test
- Clinical rapid diagnostic test
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.