- Secondary care
- Orthopedic surgery
- Humeral intramedullary nail
- Chongqing FWS Medical Devices
- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
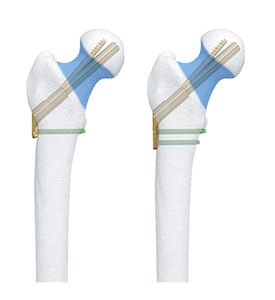
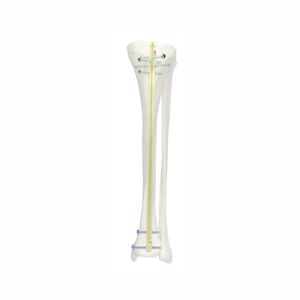
Humeral intramedullary nail SHGKproximal fixationmid-shaft fixationright
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Joint / bone
- humerus
- Fixation
- proximal fixation, mid-shaft fixation
- Side
- right, left
- Materials
- metallic
- Length
Min.: 160 mm
(6.3 in)Max.: 300 mm
(11.8 in)- Proximal diameter
7 mm, 7.5 mm, 8 mm, 8.5 mm
(0.3 in, 0.3 in, 0.3 in, 0.3 in)
Description
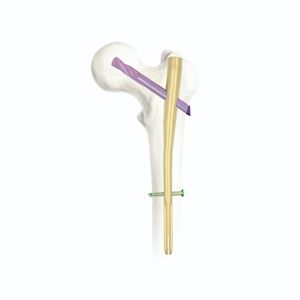
Straight main nail design with central feed point
Improving anchoring with strong subchondral bone;
Using a typical three-part fracture, insertion from the fracture area can be avoided as much as possible;
Protects the supraspinatus attachment point where the blood supply is poor;
Multi-dimensional interlocking screws
Blunt nail tip to reduce the risk of penetrating the contralateral cortex;
Stitching holes at the end of the staple to ensure reliable attachment of the rotator cuff muscles;
Nail-in-staple design for improving fixation of osteoporotic bones.
Upper row screws (humeral spur screws)
Ensure fixation of proximal humeral fractures, especially medial comminuted (inversion type) fractures.
Intelligent tools
Simplifying the procedure and saving time;
Color markings to reduce the hassle of finding parts and facilitate installation.
Scope of application
Short intramedullary nail
2 Partial surgical neck fracture;
3 Partial fracture;
4 Partial fracture;
Longer intramedullary nail
Humeral stem fracture;
Fracture of the proximal humerus extending into the diaphysis;
Proximal humerus combined with humerus;
Diaphyseal fracture.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of Chongqing FWS Medical Devices‘s catalogsExhibitions
Meet this supplier at the following exhibition(s):
Other Chongqing FWS Medical Devices products
intramedullary nail
Related Searches
- Bone plate
- Compression plate
- Metallic compression plate
- Locking compression plate
- Titanium compression plate
- Distal compression plate
- Compression bone screw
- Interbody fusion cage
- Orthopedic surgery surgery set
- Metallic compression bone screw
- Proximal compression plate
- Forearm compression plate
- Mid-shaft compression plate
- Arthrodesis nail
- Lateral compression plate
- Tibia compression plate
- General purpose compression bone screw
- PEEK interbody fusion cage
- Radius compression plate
- Humeral compression plate
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.