Opening, reaming, putting of the main nail;
Construction of the positioning frame, putting of the guide pin;
Opening proximal segment, putting of the proximal joint compression nail or spiral blade;
Distal locking according to the positioning frame, and implantation of the screw cap.
Anatomical Conformity
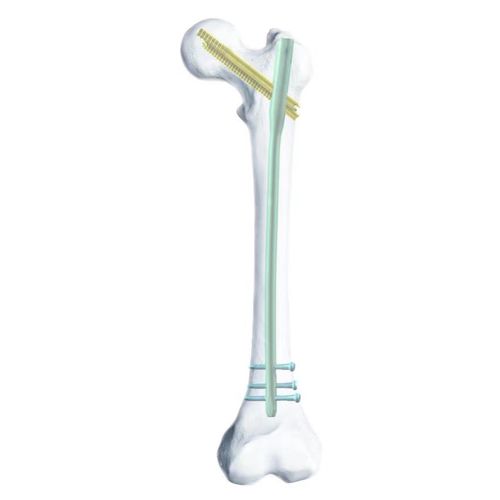
© The radius of curvature of the anterior arch increases with the length of the intramedullary nail, which meets the needs of different patients' anatomical structures and reduces the occurrence of intramedullary cam effects.
Stable Proximal Locking Nail Structure
© The femoral shaft mode locking screw angle is increased and tilted backward, which can be fixed to the lesser trochanter and increase the stability of internal fixation
© The combined interlocking double-pin mode provides the best stability, anti-rotation, anti-cut-out. anti-pull-out; when screwing in the compression nail, it produces a significant compression effect.
© The proximal trapezoidal cross-section is designed like a joint prosthesis stem for added stability and mechanical advantage
Reliable Distal Locking Structure
©Multi-planar distribution of distal locking nails, with angular arrangement between nails, from posterior lateral to anterior medial fixation, reducing the risk of withdrawal and providing better locking stability.
©The 5mm sliding pressure distance allows for postoperative phase II dynamization.
Scope of application
Standard Interlocking Mode
femoral Shaft Fracture.
Combined Compression Mode
Subtrochanteric Femoral Fractures;
Femoral neck fracture combined with femoral shaft fracture;
Intertrochanteric fracture of femur combined with femoral shaft fracture.