Medium reagent PS832for microbiologyveterinary laboratorypowder
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Type
- reagent medium
- Applications
- for microbiology, veterinary laboratory
- Format
- powder
- Micro-organism
- Pseudomonas spp
- Storage temperature
15 °C, 30 °C
(59 °F, 86 °F)
Description
Pseudomonas are ubiquitous bacteria found in the soil, on plants, in freshwater and marine habitats. Many strains can grow at low temperature (psychrophilic strains) and may contaminate food or pharmaceutical products stored in the refrigerator.
P. aeruginosa is a valid indicator for recreational water disinfection efficacy. This parameter is currently used as a criterion in the regulation of wading and swimming pools. Moreover, P. aeruginosa is important not only in terms of its role as an indicator, but also because it is an opportunistic pathogen whose transmission is often associated with water.
Other forms of Pseudomonas bacteria are known to cause food spoilage at low temperatures. These psychrophillic Pseudomonas strains include: P. fragi, which causes spoilage of dairy products, P. taetrolens which causes mustiness in eggs and P. mudicolens and P. lundensis, which cause spoilage of milk, cheese, meat, and fish, but are rarely a cause of food poisoning.
1. Fast : From 24 h incubation.
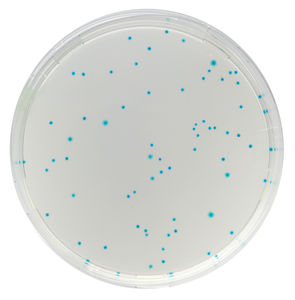
4. Simple to use : Colonies can be viewed under normal lighting conditions. Pseudomonas colonies develop with an intense blue-green colony colour, clearly visible to the naked eye.
2. Filtration method : A membrane filtration method can be used for detection from 100 mL of water, the inoculated membrane is placed, on the agar plate.
5. Easy to read : One unique intensified colour for Pseudomonas.
3. Easy preparation : The pre-weighed agar powder is mixed with the required volume of distilled water.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of CHROMagar‘s catalogsRelated Searches
- Solution reagent kit
- Molecular biology reagent kit
- Diagnostic reagent kit
- Laboratory reagent kit
- Enzyme reagent kit
- Histology reagent kit
- Reagent medium reagent kit
- Bacteria reagent kit
- Blood sample reagent kit
- Clinical reagent kit
- Microbiology reagent kit
- Tissue reagent kit
- Gene reagent kit
- Colorimetric reagent kit
- High-sensitivity reagent kit
- Metal reagent
- Escherichia coli reagent kit
- Powder reagent kit
- Environmental analysis reagent kit
- Fungi reagent kit
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.