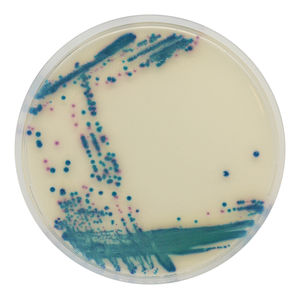
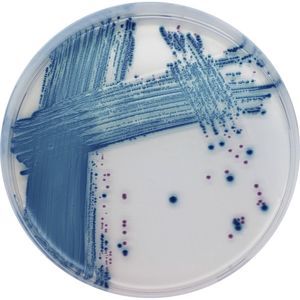
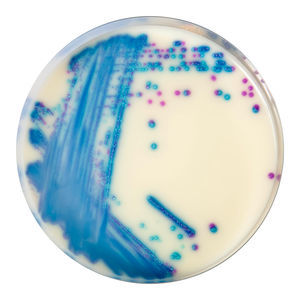
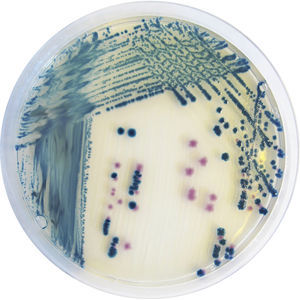
Medium reagent SB282for bacterial isolationfor urine samplesfor stool samples
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Type
- reagent medium
- Applications
- for bacterial isolation, for urine samples, for stool samples
- Micro-organism
- Streptococcus B
- Method
- chromogenic
- Other characteristics
- high-sensitivity
- Storage temperature
15 °C, 30 °C
(59 °F, 86 °F)
Description
GBS in pregnant women: The Group B Streptococci (GBS), also known under the name of Streptococcus agalactiae, are the cause of numerous infections in adults but mostly an important cause of serious neonatal infections, occuring in the three first weeks of life. Studies indicate that approximately 12-27 % of pregnant women are colonised by GBS. (WHO, Infectious diseases, Group B Streptococcus). Detecting vaginal (and in some countries also rectal) colonisation by GBS in pregnant women is the most effective strategy to prevent infection transmission during baby delivery.
Worldwide, official guidelines recommend prenatal screening of GBS in the last month of pregnancy. In GBS-carrying women, this screening allows determining the need of intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxy, which has been proved effective in preventing the infections occuring in the first week of life (known as early-onset GBS infections).
Intended Use
CHROMagar™ StrepB is a selective chromogenic culture medium that is intended to aid in the qualitative determination of Group B Streptococcus (GBS) colonization in pregnant women. This medium supports the growth of hemolytic and non-hemolytic GBS strains. The test is performed by direct, or after enrichment, plating of urine, vaginal and/or vagino/rectal swabs obtained from pregnant women. CHROMagar™ StrepB results can be interpreted after 18-24 h aerobic incubation at 35-37 °C.
CHROMagar™ StrepB is not intended to diagnose infection nor to guide nor monitor treatment for infections. Further identification, susceptibility testing and epidemiological typing is needed on suspect colonies.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of CHROMagar‘s catalogsRelated Searches
- Solution reagent kit
- Molecular biology reagent kit
- Diagnostic reagent kit
- Laboratory reagent kit
- Enzyme reagent kit
- Histology reagent kit
- Reagent medium reagent kit
- Bacteria reagent kit
- Blood sample reagent kit
- Clinical reagent kit
- Microbiology reagent kit
- Tissue reagent kit
- Gene reagent kit
- Colorimetric reagent kit
- High-sensitivity reagent kit
- Metal reagent
- Escherichia coli reagent kit
- Powder reagent kit
- Environmental analysis reagent kit
- Fungi reagent kit
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.