- Laboratory
- Laboratory medicine
- Staining solution reagent
- Dakewe (Shenzhen) Medical Equipment Co., Ltd.
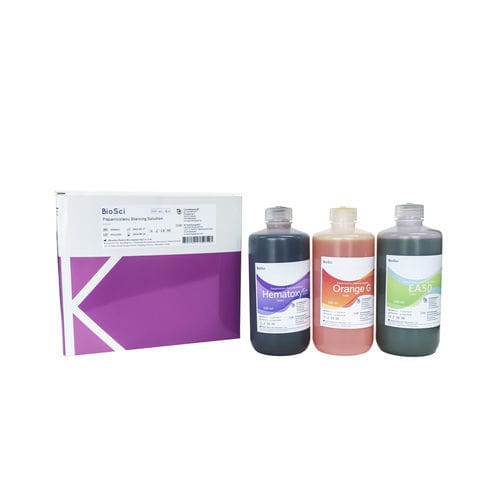
Staining solution reagent 4960411stainfor researchfor histopathology
Add to favorites
Compare this product
fo_shop_gate_exact_title
Characteristics
- Type
- staining solution, stain
- Applications
- for research, for histopathology
- Format
- liquid
- Method
- chromogenic
- Origin
- human-based
- Storage temperature
Max.: 30 °C
(86 °F)Min.: 10 °C
(50 °F)
Description
Clear nuclear structure
Color contrast
Good transparency
The cytoplasm is brightly colored
Principle of Procedure
The nucleus in the cell has a certain degree of acidity, therefore it has a strong affinity with the basic dyes (Hematoxylin), while the cytoplasm is on the contrary, which has a certain degree of basicity and a strong affinity with the acid dyes (Orange G, EA50, etc.). After Pap staining, the smears or tissue sections will be stained with different colors and intensities as follows: the nuclei will be stained purple blue and the nucleolus may be stained red. Intermediate and parabasal cells will be stained green or light blue; superficial cells will be stained pink and high keratin cells will be stained orange. Erythrocytes will show bright red or orange red, leukocytes will show light blue or light green; and the mucus will show light blue or pink.
In gynecological examination, Pap staining is the most common screening method for cervical cancer and precancerous lesions. Pap staining can also be used for observing the female hormone level and detecting reproductive tract pathogens such as Candidas and Trichomonads.
Interpretation of Test Results
Nuclei show blue purple and nucleoli may show red. Intermediate and parabasal cells show green or light blue; superficial cells show pink and high keratin cells show orange. Erythrocytes show bright red or orange red, leukocytes show light blue or light green; and the mucus show light blue or pink.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of Dakewe (Shenzhen) Medical Equipment Co., Ltd.‘s catalogsExhibitions
Meet this supplier at the following exhibition(s):


Other Dakewe (Shenzhen) Medical Equipment Co., Ltd. products
Pathological Diagnosis
Related Searches
- DAKEWE test kit
- DAKEWE solution reagent
- DAKEWE blood test kit
- DAKEWE molecular biology reagent
- DAKEWE serum test kit
- DAKEWE immunoassay test kit
- DAKEWE plasma test kit
- DAKEWE research reagent
- Diagnostic reagent kit
- DAKEWE protein reagent
- Enzyme reagent kit
- Histology reagent kit
- DAKEWE medium reagent
- Dye reagent
- Immunology reagent
- DAKEWE cytology reagent
- DAKEWE ELISA kit
- DAKEWE buffer solution reagent
- Antibody
- DAKEWE research test kit
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.