- Primary care
- General practice
- Hypodermic syringe
- General Cooperation Industry Co.,Ltd

- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
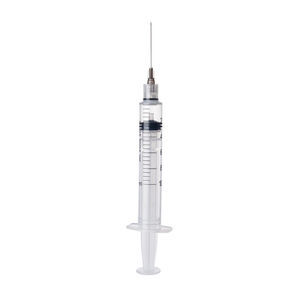
Hypodermic syringe 1 ml10 ml5 ml
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Type
- hypodermic
- Volume
- 1 ml, 10 ml, 5 ml, 20 ml, 50 ml, 2 ml, 3 mL, 30 ml, 100 ml, 2.5 ml
- Options
- disposable, sterile
Description
A syringe is a simple reciprocating pump consisting of a plunger (though in modern syringes, it is actually a piston) that fits tightly within a cylindrical tube called a barrel. The plunger can be linearly pulled and pushed along the inside of the tube, allowing the syringe to take in and expel liquid or gas through a discharge orifice at the front (open) end of the tube. The open end of the syringe may be fitted with a hypodermic needle, a nozzle or tubing to direct the flow into and out of the barrel. Syringes are frequently used in clinical medicine to administer injections, infuse intravenous therapy into the bloodstream, apply compounds such as glue or lubricant, and draw/measure liquids.
Features
-The coat is transparent, easy to observe the liquid level and air bubbles
-The 6:100 conical joint designed according to the national standard can be used with products with standard 6:100 conical joint
-The product has good sealing performance and no leakage
-Sterile, no pyrogen
-The scale ink has strong adhesion and does not fall off
-The anti-slip structure can prevent the core rod from accidentally slipping out of the jacket
Other General Cooperation Industry Co.,Ltd products
Injection and Infusion
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.