- Primary care
- Emergency medicine, Resuscitation
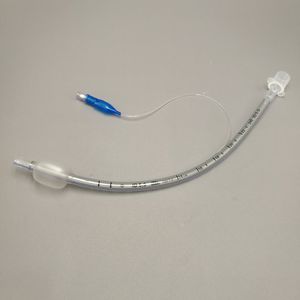
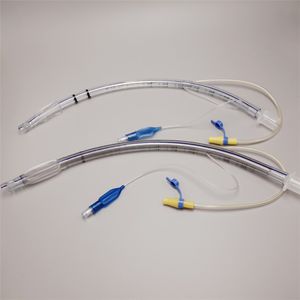
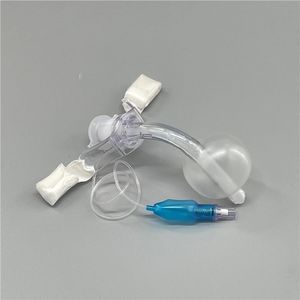
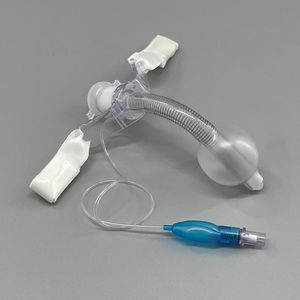
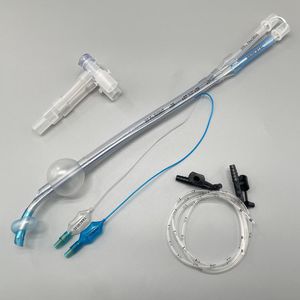
- Tracheotomy cannula
- Hangzhou Formed Medical Devices
Tracheotomy cannula





Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Medical procedure
- tracheotomy
Description
High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Treatment is a non-invasive respiratory support therapy that delivers warm, humidified, oxygen-enriched air to patients, usually using a nasal cannula.
Typically used in spontaneously breathing patients who typically require oxygen at higher flow rates.
It can provide respiratory support of patients with acute hypoxemic respiratory failure and prevent subsequent intubation when used correctly.
This greatly enhances patient comfort and ease of use.
Product Details
The features of High Flow Tracheostomy Cannula:
* Mushroom head type anti-sputum cover effectively prevents sputum splashing and pollution;
* Easy plug design of anti-sputum cover facilitates endotracheal aspiration (ETA);
* Tracheostomy interface effectively increases the positive end-expiratory pressure and ensure the positive airway pressure;
* Vent grid patent design provides adjustable airway pressure and humidification effect;
* Efficiently reduces formation of condensation;
* Compatible with most brands in the market.
Application
1. ICU
2. Emergency
3. Respiratory Department
4. Department of Anesthesiology
5. Gerontology It is designed convenient to fit, comfortable stay once fitted, providing speed and stability in High Flow Oxygen Therapy (HFOT) , and compatible with leading brands in the market.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of Hangzhou Formed Medical Devices‘s catalogsExhibitions
Meet this supplier at the following exhibition(s):

Other Hangzhou Formed Medical Devices products
Endotracheal Tube
Related Searches
- Cannula
- Suction cannula
- PVC medical mask
- Curved cannula
- Silicone medical mask
- Endotracheal tube
- Intubation cannula
- Supraglottic airway device
- Ambu bag
- Disposable cannula
- Human laryngeal mask
- Oral endotracheal tube
- Silicone laryngeal mask
- Flexible cannula
- Manual resuscitator with valve
- Tracheotomy cannula
- Disposable laryngeal mask
- Reusable medical mask
- Manual resuscitator with mask
- Silicone ambu bag
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.