- Laboratory
- Laboratory medicine
- Rapid infectious disease test
- Hangzhou GENESIS Biodetection and Biocontrol CO., LTD

- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
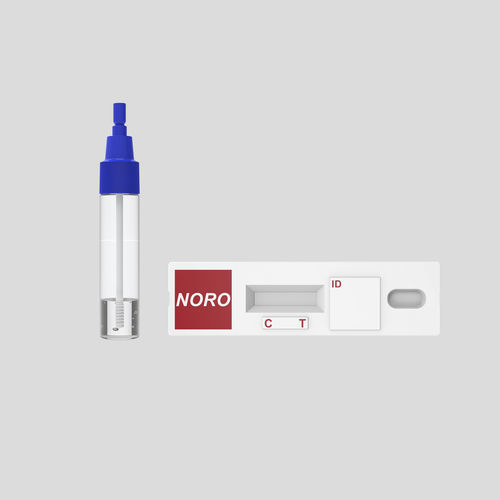
Rapid infectious disease test KaiBiLi™for antigensnorovirusfeces
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Applications
- for infectious diseases
- Tested parameter
- for antigens
- Micro-organism
- norovirus
- Sample type
- feces
- Analysis mode
- immunochromatographic
- Result display time
15 min, 30 min
- Specificity
98.2 %
- Sensitivity
95.2 %
Description
The KaiBiLiTM Norovirus Antigen Rapid Test Device is an in vitro immunochromatographic assay for the qualitative detection of norovirus antigen in human feces specimen.
Norovirus is one of the major causes of nonbacterial gastroenteritis world-wide, accounting for 19%-42% of non-bacterial diarrheal outbreaks. Illness due to this virus was initially described in 1929 as “winter vomiting disease” due to its seasonal predilection and the frequent preponderance of patients with vomiting as a primary symptom.
Noroviruses are single-stranded positive-sense RNA viruses classified as the genus Norovirus within the family Caliciviridae. Noroviruses are currently classified into five genogroups. Three of these, genogroup I, II and IV (GI, GII and GIV), occur in human infections though most noroviruses affecting humans belong to GI or GII. The norovirus is widely distributed and occurs in the form of outbreaks, with schools, hospitals and factories as the main outbreak sites. Outbreaks particularly of Norovirus associated with Winter Vomiting Disease can occur in the winter months in the western hemisphere but sporadic cases, and community and food borne outbreaks can occur throughout the year. Transmission is predominantly fecal-oral but may be airborne due to aerosolization of vomitus, which typically contains abundant infectious virus particles.
There are no age or gender differences among the outbreak patients, while the sporadic cases are mainly concentrated in children under 2 years of old and the elderly. General symptoms of norovirus infection mainly include abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, low-grade fever, systemic muscle pain and so on.
Related Searches
- Assay kit
- Solution reagent kit
- Immunoassay assay kit
- Infectious disease detection kit
- Blood rapid diagnostic test
- Diagnostic reagent kit
- Laboratory reagent kit
- Rapid lateral flow test
- Immunoassay rapid diagnostic test
- Molecular test kit
- Rapid virus test
- Respiratory infection test kit
- Serum rapid diagnostic test
- Plasma rapid diagnostic test
- Reagent medium reagent kit
- Infectious disease rapid diagnostic test
- Whole blood rapid diagnostic test
- Buffer solution reagent kit
- Lateral flow test kit
- COVID-19 detection kit
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.
