- Laboratory
- Laboratory medicine
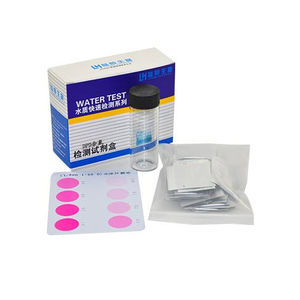
- Water analysis test kit
- Hangzhou Lohand Biological Technology Co., Ltd.
Water analysis test kit LH2037pHalkalinitynitrite
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Application field
- for water analysis
- Tested parameter
- pH, alkalinity, nitrite, sodium, acidity, metal
- Analysis mode
- biochemistry, molecular
Description
Oxygen saturation (symbol SO2) is a relative measure of the concentration of oxygen that is dissolved or carried in a given medium as a proportion of the maximal concentration that can be dissolved in that medium. It can be measured with a dissolved oxygen probe such as an oxygen sensor or an optode in liquid media, usually water. The standard unit of oxygen saturation is percent (%).
PH: pH is a measure of acidity or alkalinity.
The hydrogen ion concentration index ((hydrogen ion concentration)) refers to the ratio of the total number of hydrogen ions to the amount of total substances in the solution. It is commonly referred to as "pH", not "pH". For the determination of hydrogen ion activity index, the qualitative method can be determined by using pH indicator and pH test paper, while the quantitative pH measurement needs to be measured by pH meter.
The nitrite ion, which has the chemical formula NO−2, is a symmetric anion with equal N–O bond lengths. Upon protonation, the unstable weak acid nitrous acid is produced. Nitrite can be oxidized or reduced, with the product somewhat dependent on the oxidizing/reducing agent and its strength. The nitrite ion is an ambidentate ligand, and is known to bond to metal centers in at least five different ways.Nitrite is also important in biochemistry as a source of the potent vasodilator nitric oxide. In organic chemistry the NO−2 group is present in nitrous acid esters and nitro compounds. Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is also used in the food production industry for curing meat.Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO−3 and a molecular mass of 62.0049 u.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of Hangzhou Lohand Biological Technology Co., Ltd.‘s catalogsOther Hangzhou Lohand Biological Technology Co., Ltd. products
Lab Consumables
Related Searches
- Assay kit
- Molecular test kit
- Respiratory infection test kit
- Optical assay kit
- COVID-19 detection kit
- Test strip
- Laboratory detection kit
- Biochemistry assay kit
- Urine test strip
- Blood test strip
- Colorimetric assay kit
- PH test strip
- Strip test strip
- Metal test kit
- Electrolyte test kit
- Laboratory test strip
- Water analysis test kit
- Environmental assay kit
- Colorimetric test strip
- Water analysis test strip
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.