- Laboratory
- Laboratory medicine
- Rapid cardiovascular disease test
- Healgen Scientific

- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
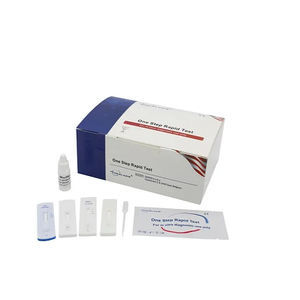
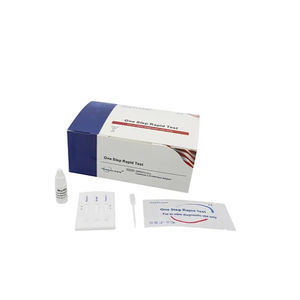
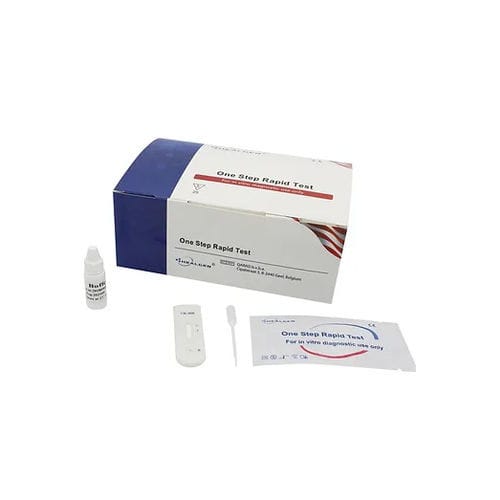
Rapid cardiovascular disease test GDCKM seriescreatine kinasebloodserum
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Applications
- for cardiovascular diseases
- Tested parameter
- creatine kinase
- Sample type
- blood, serum, plasma, whole blood, tissue
- Analysis mode
- immunoassay, lateral flow, molecular
- Format
- cassette
- Result display time
10 min
- Specificity
98.7 %
- Sensitivity
93.4 %
Description
The CK-MB Rapid Test Device (Whole Blood/Serum/Plasma) is a qualitative, lateral flow membrane based immunoassay for the detection of CK-MB in whole blood, serum or plasma. The membrane is pre-coated with capture reagent on the test line region of the test. During testing, the whole blood, serum or plasma specimen reacts with the particle coated with anti-CK-MB antibodies. The mixture migrates upward on the membrane chromatographically by capillary action to react with capture reagent on the membrane and generate a colored line. The presence of this colored line in the test line region indicated a positive result, while its absence indicated a negative result. To serve as a procedural control, a colored line will always appear in the control line region indicating that proper volume of specimen has been added and membrane wicking has occurred.
Creatine Kinase MB (CK-MB) is an enzyme present in the cardiac muscle with a molecular weight of 87.0 kDa. Creatine Kinase is a dimeric molecule formed from two subunits designated as “M” and “B” which combine to form three different isoenzymes, CK-MM, CKBB, and CK-MB. CK-MB is the isoenzyme of Creatine Kinase most involved in the metabolism of cardiac muscle tissue. The release of CK-MB into the blood following MI can be detected within 3-8 hours after the onset of symptoms. It peaks within 9 to 30 hours, and returns to baseline levels within 48 to 72 hours. CK-MB is one of the most important cardiac markers and is widely recognized as the traditional marker for the diagnosis of MI.
Exhibitions
Meet this supplier at the following exhibition(s):

Related Searches
- Assay kit
- Immunoassay assay kit
- Blood rapid diagnostic test
- Infectious disease detection kit
- Rapid lateral flow test
- Immunoassay rapid diagnostic test
- Cassette rapid diagnostic test
- Molecular test kit
- Virus rapid diagnostic test
- Serum rapid diagnostic test
- Respiratory infection test kit
- Plasma rapid diagnostic test
- Infectious disease rapid diagnostic test
- Optical assay kit
- Whole blood rapid diagnostic test
- Lateral flow test kit
- Fluorescence assay kit
- COVID-19 detection kit
- Rapid respiratory infection test
- Urine rapid screening test
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.