- Company
- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
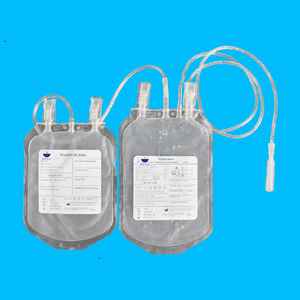
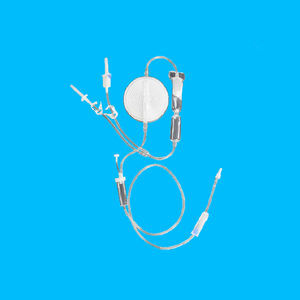
Triple blood bag CPDA-1CPD/SAG-M
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Type
- triple
- Anticoagulant
- CPD/SAG-M, CPDA-1
- Volume
Max.: 500 ml
(16.907 US fl oz)Min.: 250 ml
(8.4535 US fl oz)
Description
The Triple Blood Bag is an advanced medical device designed for the collection, preservation, and transfusion of whole blood and its components. Each bag system typically includes a primary bag with anticoagulant solution and two satellite bags for the separation of different blood components. The primary bag contains CPD (Citrate Phosphate Dextrose) or CPDA-1 (Citrate Phosphate Dextrose Adenine) solution to preserve red blood cells, while the satellite bags may contain SAGM (Saline Adenine Glucose Mannitol) or other solutions to extend the shelf life of the components.
Maximizing Efficiency in Blood Collection and Component Separation with the Triple Blood Bag
In the realm of modern healthcare, the efficient collection, separation, and preservation of blood and its components are paramount. The Triple Blood Bag stands out as an essential medical device designed to streamline these processes, ensuring safety and efficacy from collection to transfusion.
Advanced Design and Features
The Triple Blood Bag system typically comprises a primary bag containing an anticoagulant solution such as CPD (Citrate Phosphate Dextrose) or CPDA-1 (Citrate Phosphate Dextrose Adenine). These solutions play a crucial role in preserving the viability of red blood cells during storage. In addition, one of the satellite bags contains an additive solution like SAGM (Saline Adenine Glucose Mannitol), which further extends the shelf life of red blood cells up to 42 days, ensuring that blood banks can maintain a steady supply of viable blood components.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of HWTAi‘s catalogsRelated Searches
- Syringe
- Disposable syringe
- 1 ml syringe
- Sterile syringe
- 10 ml syringe
- 5 ml syringe
- PVC medical mask
- 20 ml syringe
- Oxygen mask
- Nasal cannula
- Safety syringe
- 3 mL syringe
- Oxygen nasal cannula
- 2 ml syringe
- Transparent oxygen mask
- Adjustable oxygen mask
- Dosing syringe
- Syringe without needle
- PVC oxygen mask
- Hypodermic syringe
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.