- Laboratory
- Laboratory medicine
- Rapid cardiovascular disease test
- HYSEN HANGZHOU BIOTECH

- Company
- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
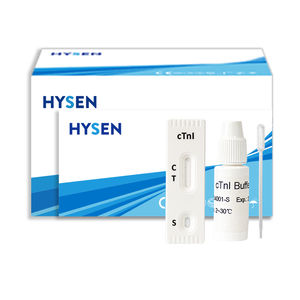
Rapid cardiovascular disease test myoglobincardiac troponin Icreatine kinase
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Applications
- for cardiovascular diseases
- Tested parameter
- myoglobin, cardiac troponin I, creatine kinase
- Sample type
- serum, plasma, whole blood
- Analysis mode
- immunochromatographic, molecular
- Format
- cassette
- Other characteristics
- self-test
- Result display time
10 min
Max.: 20 min
Min.: 10 min
- Specificity
99.8 %
Max.: 99.8 %
Min.: 98.7 %
- Sensitivity
98.6 %
Max.: 99.1 %
Min.: 96.2 %
Description
A rapid test for the diagnosis of myocardial infarction (MI) to detect Myoglobin,CK-MB and cardiac Troponin I(cTnI) qualitatively in whole blood,serum or plasma.
Myoglobin (MYO), Creatine Kinase MB (CK-MB) and cardiac Troponin I (cTnI) are proteins released into the bloodstream after cardiac injury. Myoglobin is a heme-protein normally found in skeletal and cardiac muscle with a molecular weight of 17.8 kDa. When muscle cells are damaged, Myoglobin is released into the blood rapidly due to its relatively small size. The level of Myoglobin increases measurably above baseline within 2-4 hours post-infarct,peaking at 9- 12 hours, and returning to baseline within 24-36 hours.CK-MB is an enzyme also present in the cardiac muscle, with a molecular weight of 87.0 kDa. Creatine Kinase is a dimeric molecule formed from two subunits designated as “M” and “B”, which combine to form three different isoenzymes, CK-MM, CK-BB and CK-MB. CK-MB is the isoenzyme of Creatine Kinase most involved in the metabolism of cardiac muscle tissue.The release of CK-MB into the blood following an MI can be detected within 3-8 hours after the onset of symptoms. It peaks within 9 to 30 hours, and returns to baseline levels within 48 to 72 hours. Cardiac Troponin I is a protein found in cardiac muscle, with a molecular weight of 22.5 kDa.Troponin I is part of a three subunit complex comprised of Troponin T and Troponin C. Along with tropomyosin, this structural complex forms the main component that regulates the calcium sensitive ATPase activity of actomyosin in striated skeletal and cardiac muscle. After cardiac injury occurs, Troponin I is released into the blood 4-6 hours after the onset of pain.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of HYSEN HANGZHOU BIOTECH‘s catalogsRelated Searches
- Blood rapid diagnostic test
- Rapid lateral flow test
- Immunoassay rapid diagnostic test
- Cassette rapid diagnostic test
- Rapid virus test
- Serum rapid diagnostic test
- Plasma rapid diagnostic test
- Infectious disease rapid diagnostic test
- Whole blood rapid diagnostic test
- Rapid respiratory infection test
- Urine rapid diagnostic test
- Bacteria rapid diagnostic test
- Strip rapid diagnostic test
- Rapid feces test
- Rapid drug abuse test
- Nasal rapid diagnostic test
- Nasopharyngeal rapid diagnostic test
- Rapid drug addiction test
- Self-test rapid diagnostic test
- Obstetrical/gynecological rapid test
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.