- Laboratory
- Laboratory medicine
- Solution reagent
- LINEAR CHEMICALS
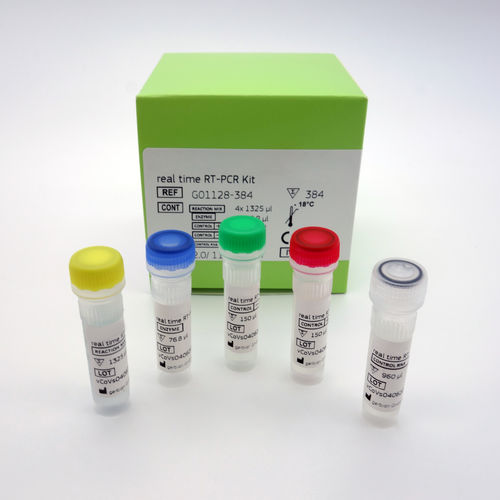
Solution reagent kit G01116-32 diagnosticfor RT-PCRliquid
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Type
- solution
- Applications
- diagnostic, for RT-PCR
- Format
- liquid
- Tested parameter
- for genes
- Micro-organism
- herpes simplex virus, VZV
- Storage temperature
Min.: -8 °C
(18 °F)-18 °C
(-0 °F)Max.: 2 °C
(36 °F)
Description
The virellaHSV/VZV real time PCR is an assay for the amplification and differentiation of purified DNA of Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1), Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2) and Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV), extracted from biological specimens.
2 Background Information
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 and Type 2
The herpes simplex virus, or herpes, is categorized into 2 types: herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) and herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). HSV-1 is mainly transmitted by oral-to-oral contact to cause oral herpes (which can include symptoms known as “cold sores”), but can also cause genital herpes. HSV-2 is a sexually transmitted infection that causes genital herpes. Both HSV-1 and HSV-2 infections are lifelong. An estimated 3.7 billion people under age 50 (67%) have HSV-1 infection globally. An estimated 417 million people aged 15-49 (11%) worldwide have HSV-2 infection. Most oral and genital herpes infections are asymptomatic. Symptoms of herpes include painful blisters or ulcers at the site of infection.
Herpes infections are most contagious when symptoms are present but can still be transmitted to others in the absence of symptoms. Infection with HSV-2 increases the risk of acquiring and transmitting HIV infection. In immunocompromised people, such as those with advanced HIV infection, HSV-1 can have more severe symptoms and more frequent recurrences. Rarely, HSV-1 infection can also lead to more severe complications such as encephalitis or keratitis (eye infection). Neonatal herpes can occur when an infant is exposed to HSV in the genital tract during delivery.
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of LINEAR CHEMICALS‘s catalogsRelated Searches
- Assay kit
- LiNEAR solution reagent
- Blood assay kit
- LiNEAR molecular biology reagent
- Immunoassay assay kit
- Plasma assay kit
- Infectious disease detection kit
- LiNEAR rapid blood test
- LiNEAR protein reagent
- LiNEAR diagnostic reagent
- LiNEAR laboratory reagent
- Rapid lateral flow test
- Immunoassay rapid diagnostic test
- LiNEAR cassette rapid test
- LiNEAR rapid virus test
- LiNEAR rapid serum test
- LiNEAR rapid plasma test
- Histology reagent kit
- LiNEAR medium reagent
- LiNEAR rapid infectious disease test
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.