IgG reagent GT22107for scientific researchfor Western blotimmunohistochemistry
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Type
- IgG
- Applications
- for scientific research, for Western blot, immunohistochemistry, for immunofluorescence, for immunocytochemistry
- Format
- liquid
- Tested parameter
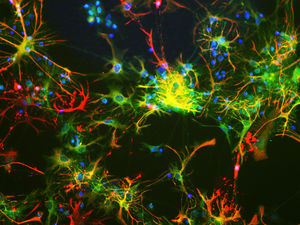
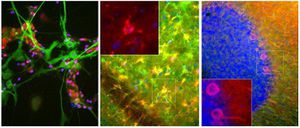
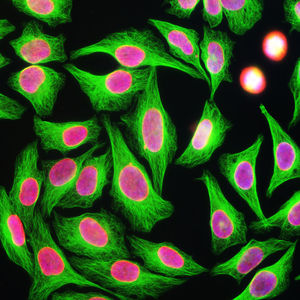
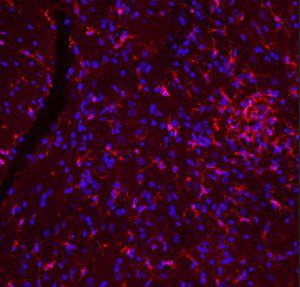
- GFAP
- Storage temperature
Min.: -20 °C
(-4 °F)Max.: 4 °C
(39 °F)
Description
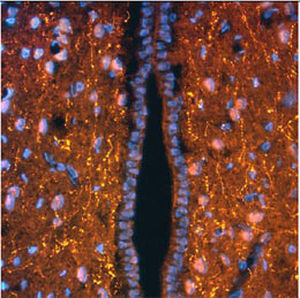
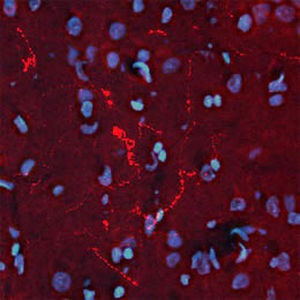
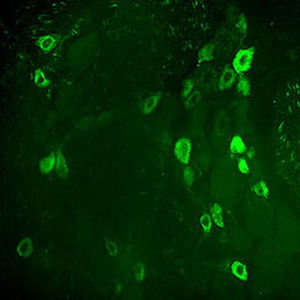
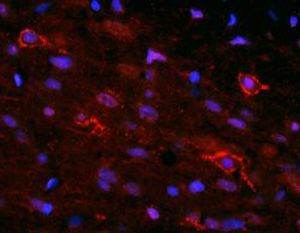
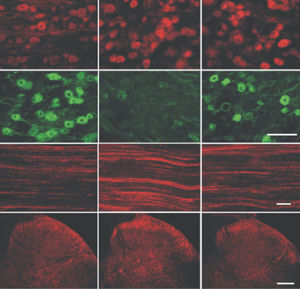
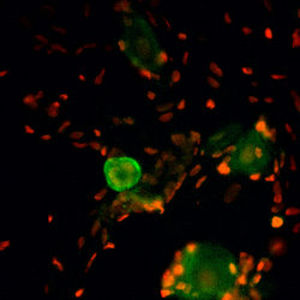
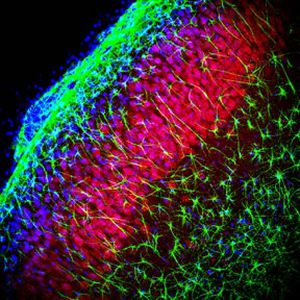
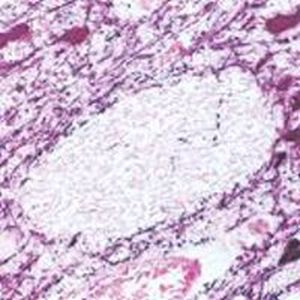
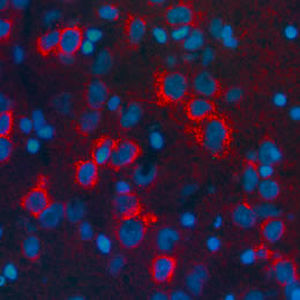
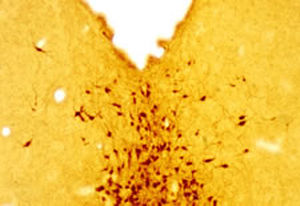
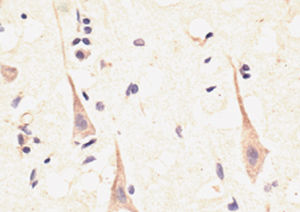
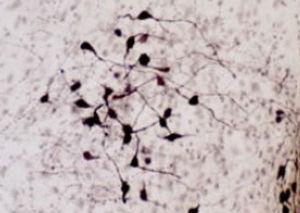
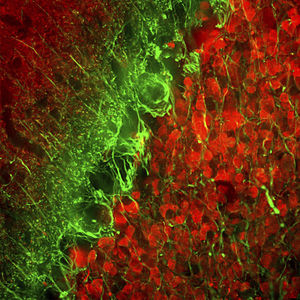
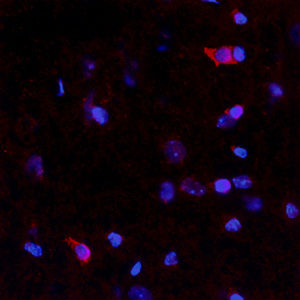
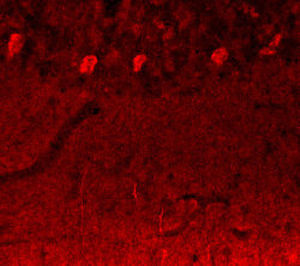
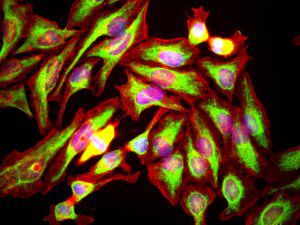
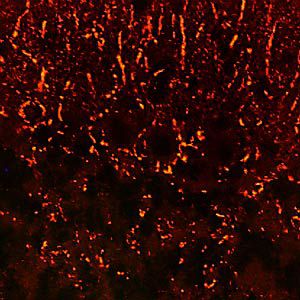
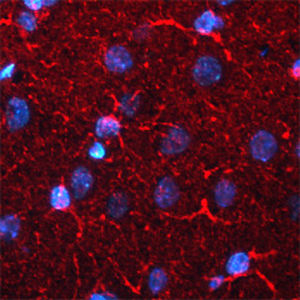
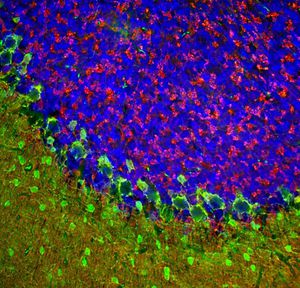
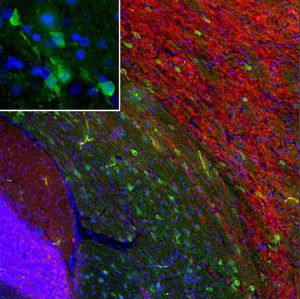
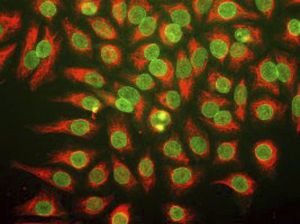
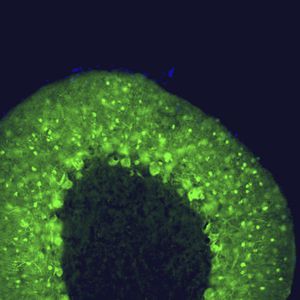
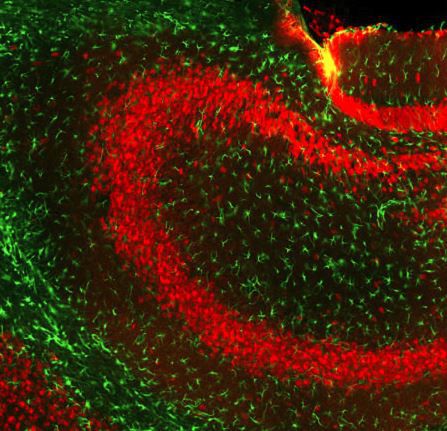
Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) is a major CNS protein which runs on SDS-PAGE as a ~50kDa protein, usually associated with somewhat lower molecule weight bands which are alternate transcripts from the single gene or in vivo proteolytic fragments. GFAP is strongly and specifically expressed in astrocytes and certain other glia in the central nervous system, in satellite cells in peripheral ganglia, in non-myelinating Schwann cells in peripheral nerves and is also a useful marker of neural stem cells. Astrocytes respond to many damage and disease states resulting in “astrogliosis” or the presence of a “glial response”. GFAP antibodies are widely used to study reactive astrocytes which form part of this response, since these cells stain much more strongly with GFAP antibodies than normal astrocytes. GFAP also forms a major component of the so-called glial scar, an astrocyte rich structure apparently forming part of the barrier to nerve fiber regeneration following damage in the central nervous system. Neural stem cells frequently strongly express GFAP but many lose this if they develop into neurons or oligodendrocytes. Finally, Alexander disease was recently shown to be caused by point mutations in the protein coding region of the GFAP gene. All forms of Alexander disease are characterized by the presence of Rosenthal fibers, which are GFAP containing cytoplasmic inclusions found in astrocytes.
Catalogs
GT22107
1 Pages
Related Searches
- Molecular biology reagent kit
- Research reagent kit
- Analysis software
- Protein reagent kit
- Immunology reagent
- Antibody
- Laboratory software
- Lyophilized reagent kit
- Serum reagent kit
- Immunohistochemistry reagent kit
- Enzyme reagent
- Monoclonal antibody reagent kit
- Western blot reagent kit
- Scientific research reagent kit
- Research software
- Immunofluorescence reagent kit
- Polyclonal antibody
- Cytokine reagent kit
- Growth factor reagent kit
- Mouse-based reagent
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.