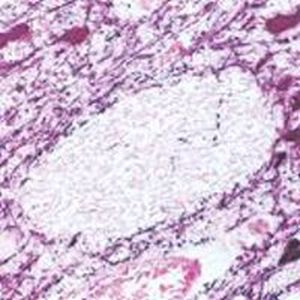
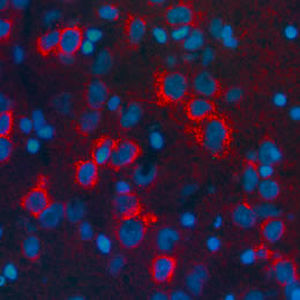
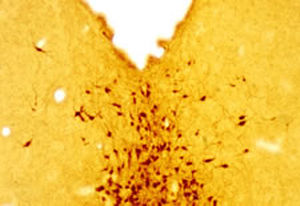
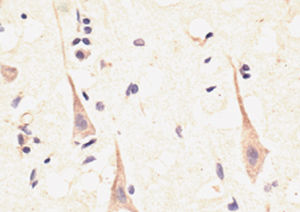
IgG reagent RA20072for scientific researchimmunohistochemistrylyophilized
Add to favorites
Compare this product
fo_shop_gate_exact_title
Characteristics
- Type
- IgG
- Applications
- for scientific research, immunohistochemistry
- Format
- lyophilized
- Origin
- rabbit-based
- Storage temperature
Min.: -20 °C
(-4 °F)Max.: 4 °C
(39 °F)
Description
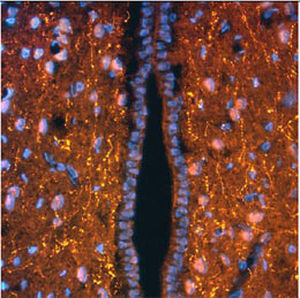
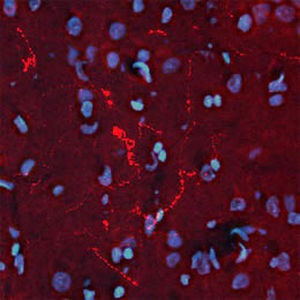
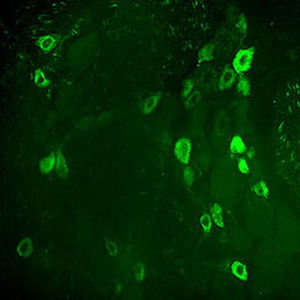
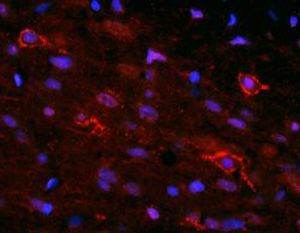
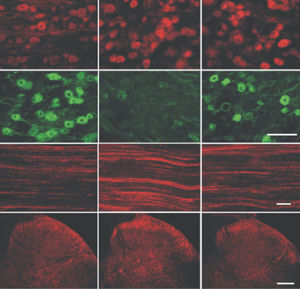
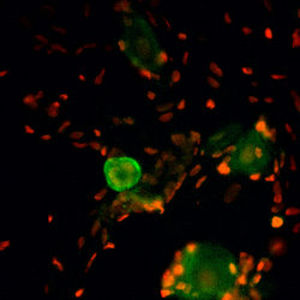
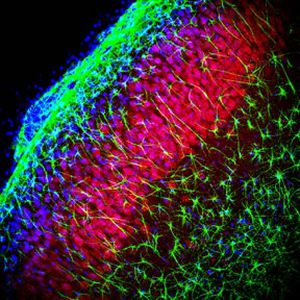
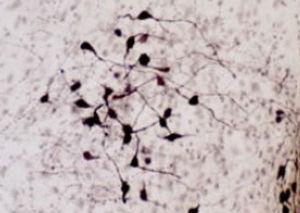
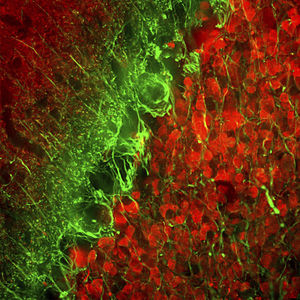
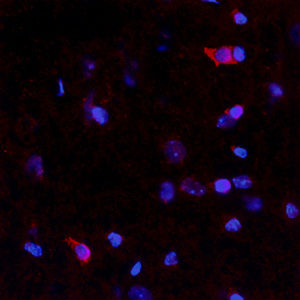
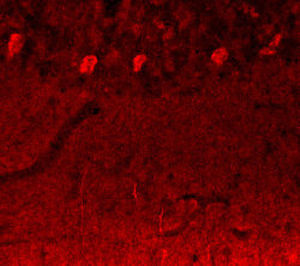
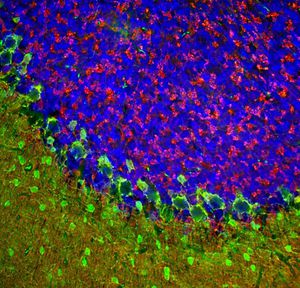
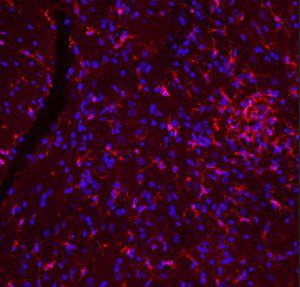
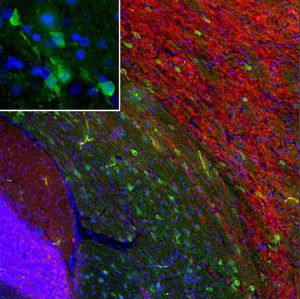
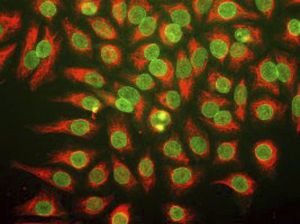
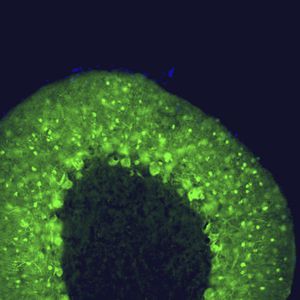
Neurotensin is a 13-amino acid neuropeptide involved in neurotransmission in the CNS and PNS. In the CNS, it interacts with dopamine. It also plays a tonic stimulatory role on HPA axis activity and an inhibitory effect on vasopressin secretion. Through its diverse expression, Neurotensin modulates analgesia, hypothermia, appetite, fear response, gut motility and locomotor activity.
By selective targeting or blockade of specific neurotensin receptors, investigators have identified potential drugs for use in the treatment of schizophrenia, alcoholism, chronic pain, or cancer.
Catalogs
RA20072
2 Pages
Related Searches
- Molecular biology reagent kit
- Research reagent kit
- Analysis medical software
- Protein reagent kit
- Immunology reagent
- Antibody
- Laboratory software
- Lyophilized reagent kit
- Serum reagent kit
- Immunohistochemistry reagent kit
- Enzyme reagent
- Scientific research reagent kit
- Monoclonal antibody reagent kit
- Western blot reagent kit
- Research software
- Immunofluorescence reagent kit
- Cytokine reagent kit
- Polyclonal antibody
- Growth factor reagent kit
- Mouse-based reagent
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.