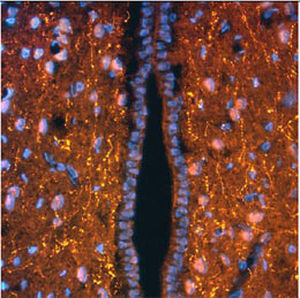
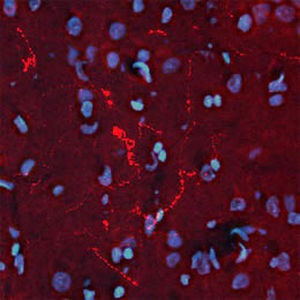
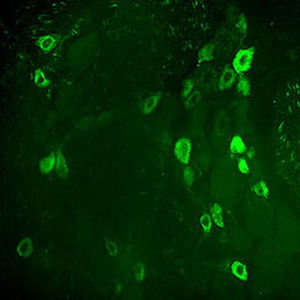
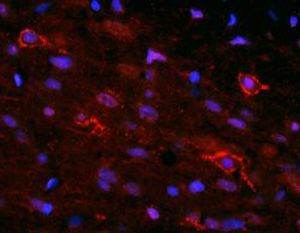
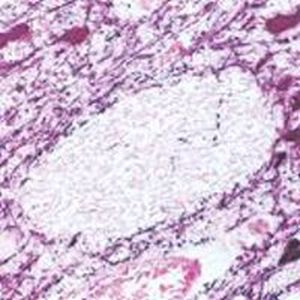
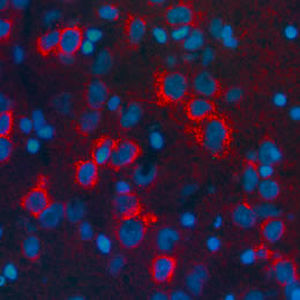
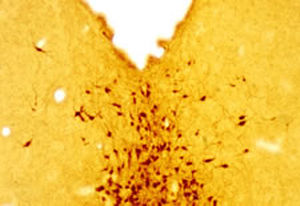
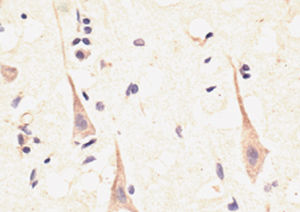
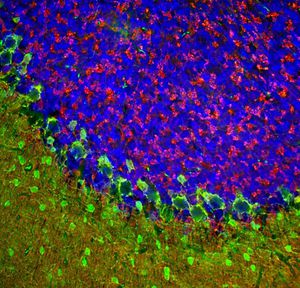
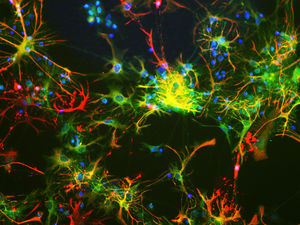
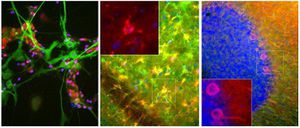
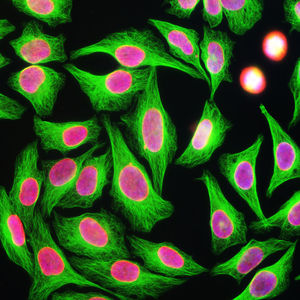
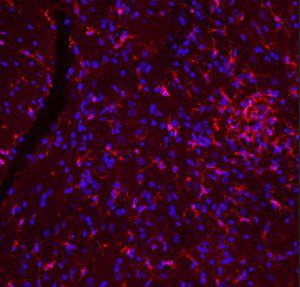
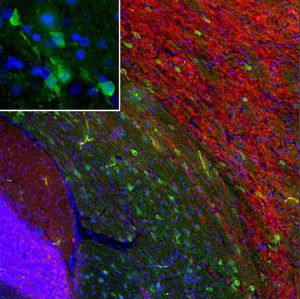
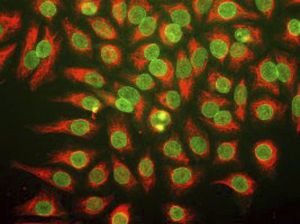
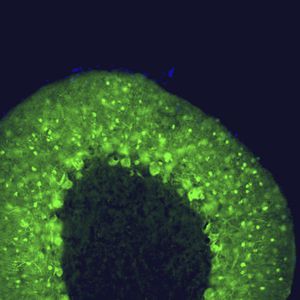
Antibody CH22139for Western blotimmunohistochemistryfor immunofluorescence
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Type
- antibody
- Applications
- for Western blot, immunohistochemistry, for immunofluorescence, for immunocytochemistry
- Format
- liquid
- Tested parameter
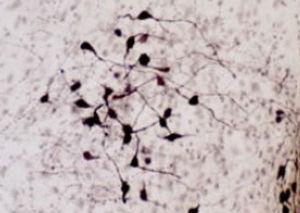
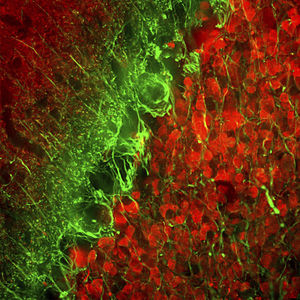
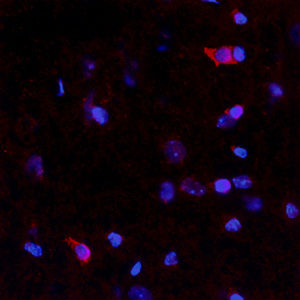
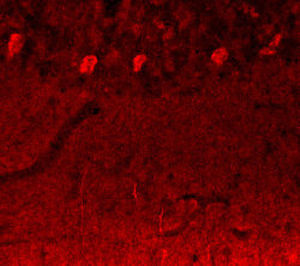
- for alpha-synuclein
- Storage temperature
Min.: -20 °C
(-4 °F)Max.: 4 °C
(39 °F)
Description
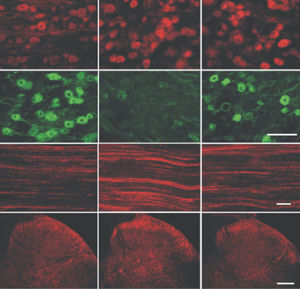
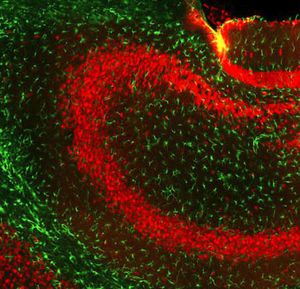
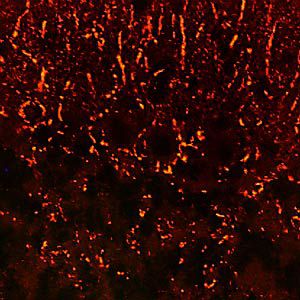
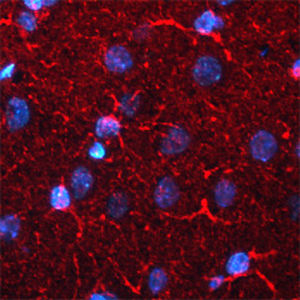
α-synuclein is a member of the synuclein protein family, the other two members being β and γ synuclein, each protein being coded for by a distinct but related gene. α-synuclein was originally isolated as a major synaptic vesicle associated protein from the electric organ of the fish Torpedo, and direct homologues of α-synuclein are found in all vertebrates. Later work connected α-synuclein expression with several human brain pathologies, so that it is a major component of the Lewy bodies of Parkinson’s disease. Point mutations of α-synuclein proved to be causative of some forms of familial Parkinson’s disease. α-synuclein is also found in the Lewy bodies of patients with diffuse Lewy body disease and inclusions in glial cells in the brains of patients with multiple system atrophy and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. α-synuclein is normally heavily expressed in brain and appears to be localized primarily to presynaptic regions, though not with a typical synaptic vesicle distribution pattern.
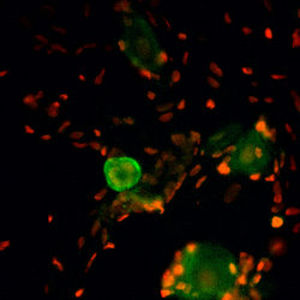
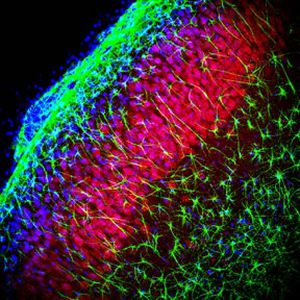
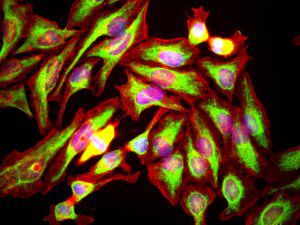
This antibody recognizes full length human and rodent α-synuclein specifically both in western blots and in immunocytochemical experiments and is a good marker of synapses on transgenic mice.
Catalogs
CH22139
1 Pages
Related Searches
- Molecular biology reagent kit
- Research reagent kit
- Analysis software
- Protein reagent kit
- Immunology reagent
- Antibody
- Laboratory software
- Lyophilized reagent kit
- Serum reagent kit
- Immunohistochemistry reagent kit
- Enzyme reagent
- Monoclonal antibody reagent kit
- Scientific research reagent kit
- Western blot reagent kit
- Research software
- Immunofluorescence reagent kit
- Polyclonal antibody
- Cytokine reagent kit
- Growth factor reagent kit
- Mouse-based reagent
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.