- Laboratory
- Laboratory medicine
- Malaria test kit
- RainSure Scientific

- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
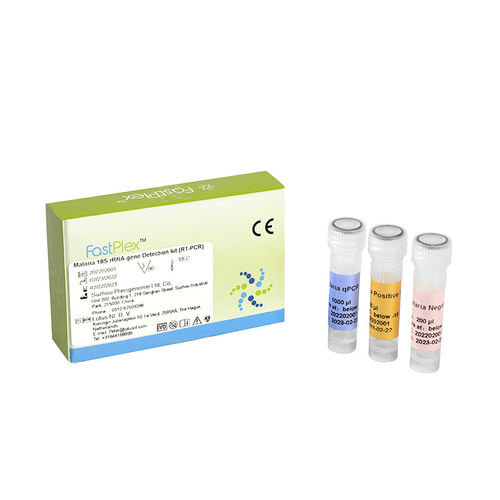
Malaria detection kit 3.02.03.0002for genesbloodfor RT-PCR
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Applications
- malaria
- Tested parameter
- for genes
- Sample type
- blood
- Analysis mode
- for RT-PCR
Description
alaria is an infectious disease transmitted to humans by an infected female Anopheles mosquito. It is typically confirmed through the microscopic examination of blood smears or antigen-based rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs).
In low-intensity transmission areas, a parasite level in the blood greater than 100,000 per microliter, or in high-intensity transmission areas, greater than 250,000 per microliter, can be diagnosed as malaria. The accuracy of blood smears ranges from 75% to 90% under optimal conditions but can be as low as 50%. In contrast, RDTs are often more accurate in predicting the presence of malaria parasites. However, their diagnostic accuracy and specificity vary widely depending on the manufacturer, and they are unable to determine the parasite count. To enhance analytical accuracy and enable quantification across a broader range of parasite densities, PCR for malaria has been developed in the past decade.
RainSure Malaria 18S rRNA Gene Detection Kit (RT-PCR) provides sensitivity, fast detection, and quantitative analysis for four types of malaria parasites.
Related Searches
- Assay kit
- Solution reagent kit
- Blood assay kit
- Molecular biology reagent kit
- Serum assay kit
- Plasma assay kit
- Infectious disease detection kit
- Laboratory reagent kit
- Enzyme reagent kit
- Molecular test kit
- Clinical assay kit
- PCR reagent kit
- Cell assay kit
- Oncology test kit
- Genetic test kit
- Tissue detection kit
- Oncology test kit
- RT-PCR detection kit
- Taq DNA polymerase reagent kit
- Hematology test kit
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.