- Surgery unit
- Anesthesia
- Anesthesia mask
- RVENT Medikal

- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
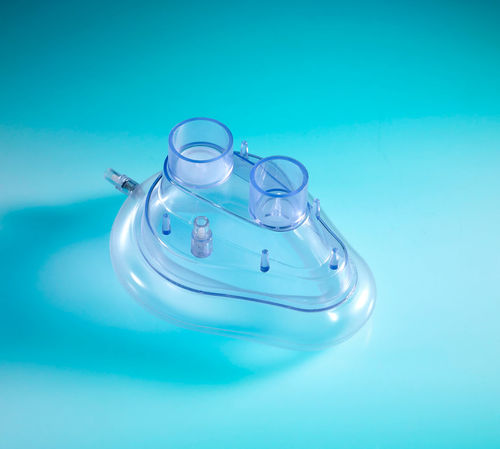
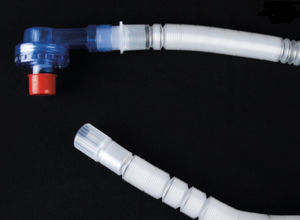
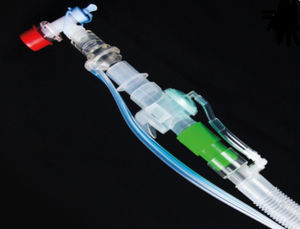
CPAP anesthesia mask 10004069
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Ventilation mode
- CPAP
Description
Continous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) is the method of ventilating a patient applying higher pressure than enviromental atmospheric pressure to the airways of the patient to improve oxygenation via ventilator or CPAP machine.
CPAP prevents early end-expiratory closure of the airways and alveolar collapse
Today CPAP is routinely used for mechanically ventilated patients or spontaneously breathing respiratory patients to improve the oxgenation
Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, ARDS, Post-operative atelectasis
Acute respiratory distress, COPD, Cardiogenic pulmonary oedema
Post-extubation hypoxemia, Weaning
Catalogs
No catalogs are available for this product.
See all of RVENT Medikal‘s catalogsExhibitions
Meet this supplier at the following exhibition(s):

*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.