- Laboratory
- Laboratory medicine
- Rapid thrombosis test
- SCREEN ITALIA
- Company
- Products
- Catalogs
- News & Trends
- Exhibitions
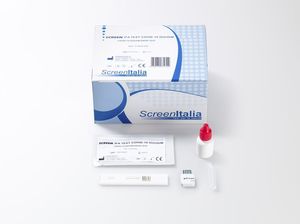
Rapid thrombosis test SC-1583-20D-dimerbloodimmunofluorescence
Add to favorites
Compare this product
Characteristics
- Applications
- for thrombosis
- Tested parameter
- D-dimer
- Sample type
- blood
- Analysis mode
- immunofluorescence
- Format
- cassette
- Other characteristics
- with digital reader
- Result display time
15 min
Description
SCREEN IFA TEST D-DIMERO
Fluorescence Immunoassay D-Dimer)
REF: SC-1583-20
Rapid test for measuring D-Dimer in whole blood or plasma with the use of Screen® Immunofluorescence Analyzer. For professional in vitro diagnostic use only. D-dimer (or D dimer) is a breakdown product of fibrin (or FDP), a small protein fragment found in the blood after a blood clot has been degraded by fibrinolysis. Its formation or increase reflects the activation of coagulation and the fibrinolysis system, and its level in plasma can represent the production of the active agent of thrombin fibrin in vivo. It can be used as an indicator of thrombosis in the physique. The D-Dimer content in thrombotic patients is significantly elevated. D-dimer (or D dimer) is a breakdown product of fibrin (or FDP), a small protein fragment found in the blood after a blood clot has been degraded by fibrinolysis. Its formation or increase reflects the activation of coagulation and the fibrinolysis system, and its level in plasma can represent the production of the active agent of thrombin fibrin in vivo. It can be used as an indicator of thrombosis in the physique. The D-Dimer content in thrombotic patients is significantly elevated. Furthermore, some studies have shown that low D-Dimer levels (0.1-0.5 mg/L) are closely related to the presence of cardiovascular disorders and high D-Dimer levels may be early indicators for excluding DVT and PE.
Catalogs
SCREEN CATALOGUES EN
182 Pages
Related Searches
- Assay kit
- Blood assay kit
- Immunoassay assay kit
- Blood rapid diagnostic test
- Rapid lateral flow test
- Immunoassay rapid diagnostic test
- Cassette rapid diagnostic test
- Virus rapid diagnostic test
- Serum rapid diagnostic test
- Respiratory infection test kit
- Plasma rapid diagnostic test
- Infectious disease rapid diagnostic test
- Whole blood rapid diagnostic test
- Cassette assay kit
- Lateral flow test kit
- COVID-19 detection kit
- Rapid respiratory infection test
- Urine rapid screening test
- Antigen assay kit
- Test strip
*Prices are pre-tax. They exclude delivery charges and customs duties and do not include additional charges for installation or activation options. Prices are indicative only and may vary by country, with changes to the cost of raw materials and exchange rates.